The structural and sequence motifs refer to short segments of protein three-dimensional structure or amino acid sequence that were found in a large number of different proteins Supersecondary structure. Different proteins are made of different combinations of amino acids.
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
A the peptide bonds linking amino acids differ from protein to protein.

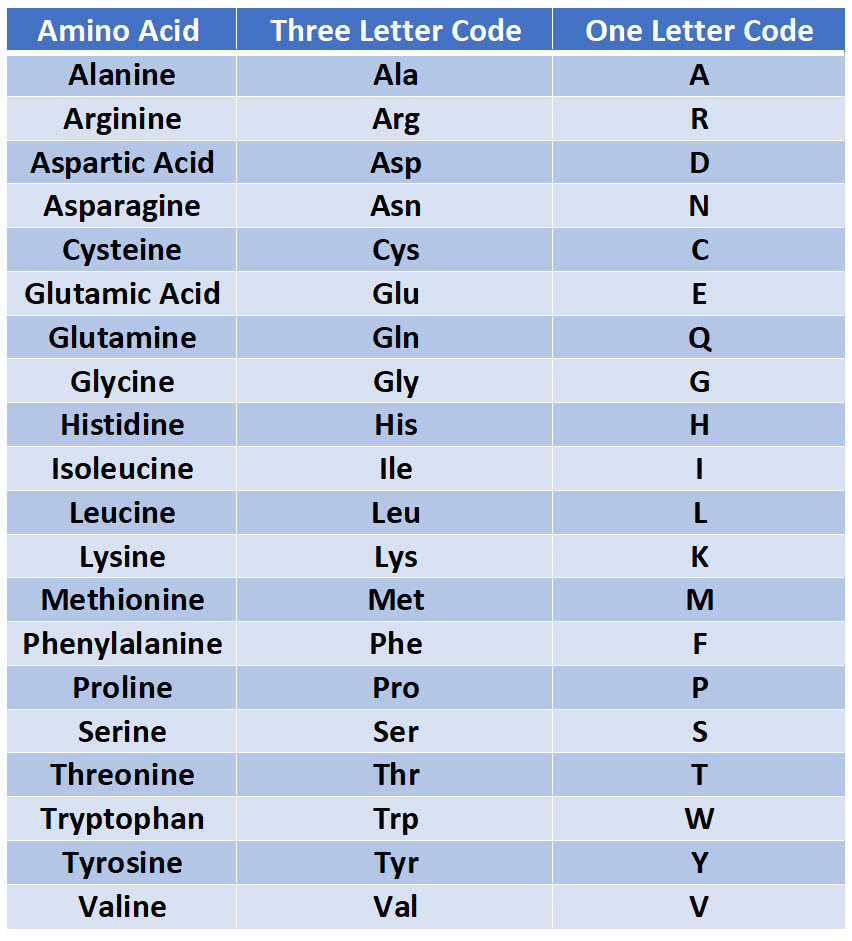
. Protein synthesis takes place within the nucleus and ribosomes of a cell and is. Alpha helix and beta pleated sheet. 20 amino acids are commonly found in proteins in each kind of protein contains a different number comma combination and sequence of amino acids which gives proteins their specific functions and unique characteristics in food.
For each cytochrome c molecule from different organisms that has been sequenced to date 37 of these amino acids appear in the same position in all samples of cytochrome c. Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary. Figure 6 Bovine serum insulin is a protein hormone made of two peptide chains A 21 amino acids long and B 30 amino acids long.
Stion 28 15 points 9045 There are 20100 different possible sequence combinations for a protein chain with 100 amino acids. All amino acids have the alpha carbon bonded to a hydrogen atom carboxyl group and an amino group. Because the number of amino acids and their exact sequence in the polypeptide chain is different for each protein.
The ability of different proteins to assume a wide range of distinct three-. This indicates that there may have been a common ancestor. D the number of nucleotides found in each protein varies from molecule to molecule.
The sequence of amino acids in the chain determines how the chain will fold. Amino acid and protein structure. The sequences of amino acids in the A and B chains are unique to insulin.
C the peptide bonds linking amino acids differ from protein to protein D each protein contains its own unique sequence of sugar molecules. For example hemoglobin is a combination of four polypeptide subunits. Any change in the sequence changes the entire protein.
This is called the primary structure and it determines the. Proteins differ from one another because A the number of nucleotides found in each protein varies from molecule to molecule B the sequence of amino adds in the polypeptide chain differs from protein to protein. On comparing the human and chimpanzee protein sequences no sequence difference was found.
Size of a codon. Proteins are large complex biomolecules that play many critical roles in biological bodies. The key difference between DNA and protein sequence is that the DNA sequence is a series of deoxyribonucleotides bonded via phosphodiester bonds while the protein sequence is a series of amino acids bonded via peptide bonds.
TRNAs serve as an adaptor for translating from nucleic acid to protein. Overview of protein structure. Give the number and type of hybrid orbital that forms when each set of atomic orbitals mixes.
The supersecondary structure refers to a specific combination of secondary structure elements such as β-α-β units or a helix-turn-helix. The proteins differ from each other in their variety number and order of their constituent amino acids linked by peptide bonds only. These Sequences are the arrangement of amino acids in a protein held together by peptide bondsProteins can be made from 20 different kinds of amino acids and the structure.
The N terminal amino acid of the A chain is glycine whereas the C terminal amino acid is asparagine. The order of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. B the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain differs from protein to protein.
Proteins differ in the number combinations and sequence of. If the protein is subject to changes in temperature pH or exposure to chemicals the protein structure may change losing its shape in what is known as denaturation as discussed earlier. - The combination of a number of different polypeptide chains and associated non-protein prosthetic groups into a large complex protein molecule.
DNA is a type of nucleic acid. The sequence of amino acids in its polypeptide chain. The exact sequence of the proteins is very important as it determines the final fold and therefore the function of the protein.
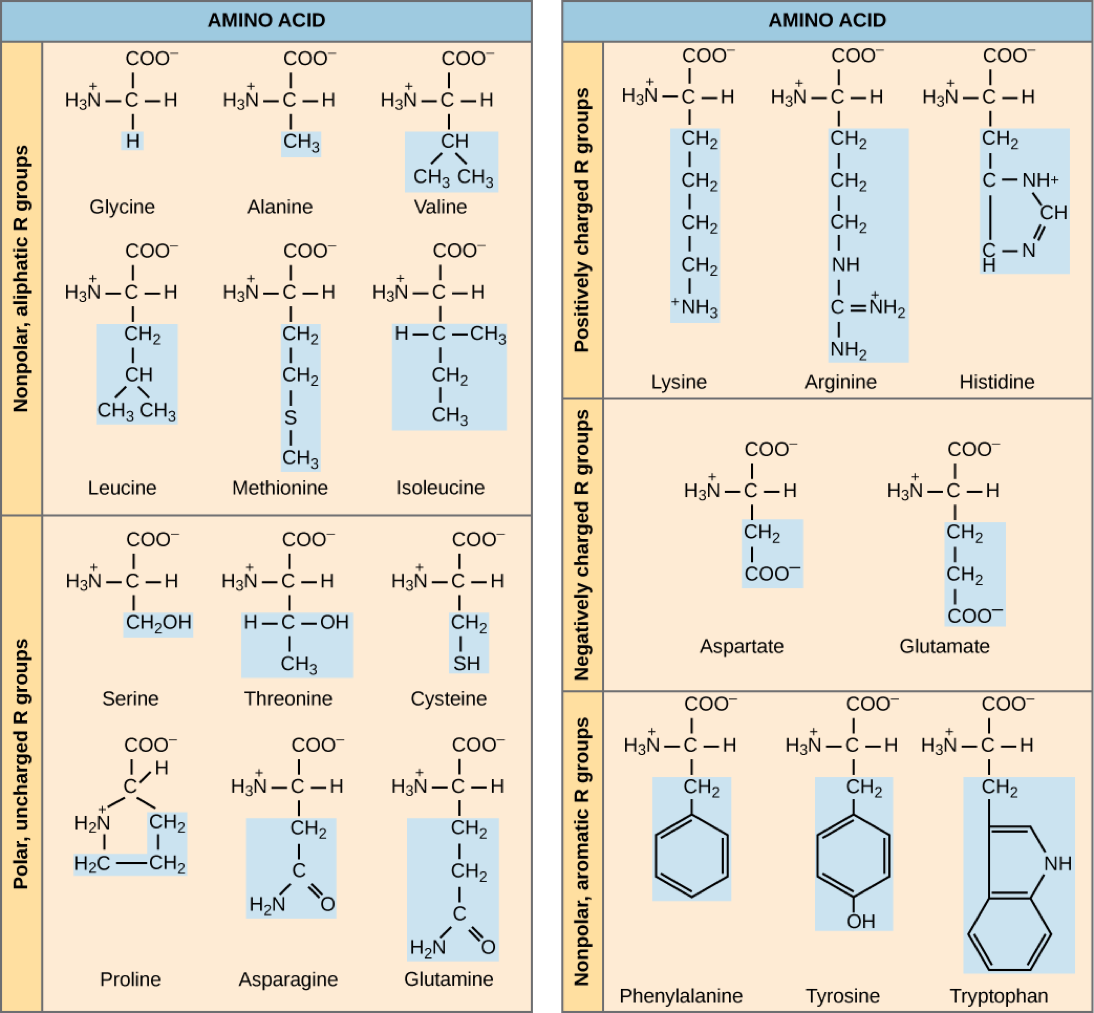
Therefore it is the sequence of the chemically different side chains Panel 3-1 The 20 Amino Acids Found in Proteins. The machinery for synthesizing proteins under the direction of template mRNA is the ribosome. The R group varies among amino acids and determines the differences between these protein monomers.
Introduction to proteins and amino acids. In contrast the protein in Figure 4 looks quite different from the proteins in Figures 2 and 3. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
Protein synthesis is process in which polypeptide chains are formed from coded combinations of single amino acids inside the cell. In addition to the amino acid sequence of the protein what ther factors INCREASE the potential for diversity in these macromolecules. - The sequence of amino acids found in its polypeptide chains.
This is because the three-dimensional structures of proteins are highly varied. The synthesis of new polypeptides requires a coded sequence enzymes and messenger ribosomal and transfer ribonucleic acids RNAs. The number of polypeptide chains together form proteins.
Always has the same three-dimensional shape. Get more out of your subscription Access to over 100 million course-specific study resources. The amino acid sequence of a protein is determined by the information found in the cellular genetic code.
Each type of protein differs in its sequence and number of amino acids. All amino acids have the same basic structure. Each protein has its own unique sequence and shape held together by chemical interactions.
These chains have amino acids arranged in a particular sequence which is characteristic of the specific protein. C each protein contains its own unique sequence of sugar molecules. The directionality of amino acids being added the planar nature of the peptide bond noncovalent.
Three is the minimum number of nucleotides per codon needed to encode 20 amino acids. Proteins are made up of one or more long chains of amino acid sequences. Introduction to amino acids.
- Shape of one protein molecule different from all other types. Proteins differ from carbohydrates and lipids in that they contain _____. The building blocks of proteins are _____.
A one p and one s b three p one d and one s. Orders of protein structure.
How Are Proteins Distinguished From Each Other Pediaa Com
Protein Structure Nutrition Science And Everyday Application

0 Comments